Web crawling, also known as web scraping, is the process of automatically extracting data from websites. It allows us to gather valuable information from various sources on the internet efficiently and in a structured manner. In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of web crawling and how you can get started with your own data extraction projects.

What if I told you that web crawling could come to your rescue even in unexpected work scenarios? 🤔
Imagine you’re on a relaxing weekend, enjoying your favorite Netflix series, when suddenly your boss calls with an urgent task.
Let’s say your boss needs a comprehensive analysis of competitors’ pricing for an upcoming project. Manually collecting this data from various websites would be time-consuming and error-prone. However, with web crawling, you can automate the data extraction process, quickly gathering pricing information from multiple sources and generating a detailed report. Not only does this save you hours of manual work, but it also ensures accuracy and provides valuable insights for your boss.
Web crawling can be a game-changer in various work scenarios. Need to gather customer reviews for a product launch? Web crawling can swiftly scrape reviews from e-commerce platforms, allowing you to analyze sentiment and make data-driven decisions. Want to monitor industry trends or track news updates? Web crawling can continuously fetch relevant information from news websites, keeping you up to date and enabling you to stay ahead of the competition.
Benefits
Let's have a look at the various benefits of web crawling that have made it a popular concept for seamless integration within large-scale enterprises.
Process of Web Crawling
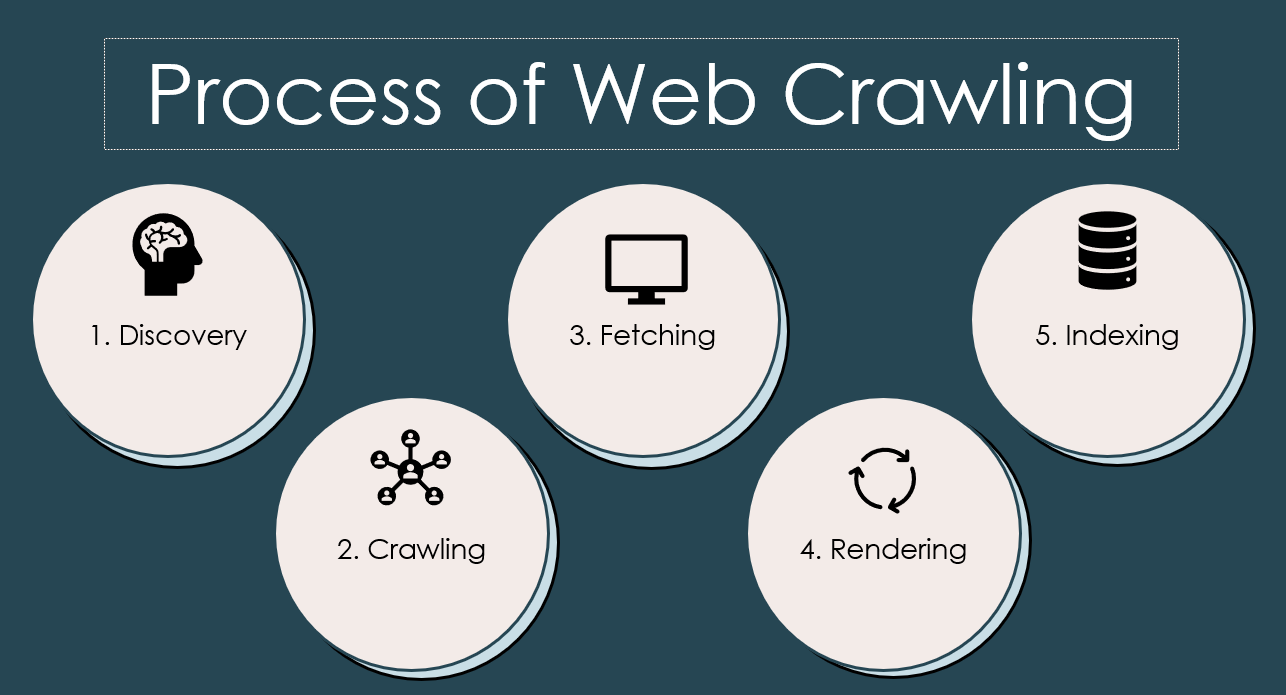
💡 Discovery
🕷️ Crawling
⛏️ Fetching
💻 Rendering
📑 Indexing
It’s important to note that web crawling is an iterative process. As the crawler discovers new links during the crawling stage, it adds them to the queue for subsequent crawling, continuing the process of discovery, crawling, fetching, rendering, and indexing for a broader coverage of the web.
Getting Started with Web Crawling
Identify Your Data Needs: Determine the specific information you want to extract from websites. It could be product details, contact information, news articles, or any other relevant data.
Choose a Web Crawling Tool: There are various web crawling frameworks and libraries available, such as BeautifulSoup and Scrapy in Python. Select a tool that aligns with your programming language and project requirements.
You can learn more about Python Scrapy here
Understand the Website Structure: Familiarize yourself with the target website’s structure. Identify the HTML elements that contain the data you need, such as class names, IDs, or specific tags. Some key steps to follow here may include:
1. Inspect the web page
2. Explore the HTML Elements
3. Identify unique Identifiers
Example: <div class="product-name">
Write the Crawling Code: Utilize your chosen web crawling tool to write code that navigates through the website, locates the desired data, and extracts it. This involves sending HTTP requests, parsing HTML content, and selecting the relevant elements.
Handle Website-Specific Challenges: Some websites may implement anti-crawling measures like CAPTCHA or rate limiting. Implement strategies like rotating IP addresses or adding delays in your crawling code to handle such challenges.
Ethical Considerations
While web crawling can be a powerful tool for data extraction, it’s important to respect website owners’ terms of service and adhere to ethical guidelines. Always ensure that your crawling activities are legal and ethical. Be mindful of any website-specific crawling policies and consider reaching out to website owners for permission when necessary.
Conclusion
Web crawling opens up a world of possibilities for data extraction and analysis. By automating the process of gathering data from websites, you can save time and collect valuable insights. Armed with the knowledge from this beginner’s guide, you’re ready to embark on your web crawling journey. Remember to stay ethical, explore different tools, and continue learning as you dive deeper into the exciting world of web crawling.
